- Fueling the future of Greater Indiana.
- [email protected]
The Mission:
EDUCATE STATEWIDE
 Experience an Electric Vehicle at a local ride & drive, learn about state and utility incentives, and access tools, training, and other resources for dealerships and commercial fleets across the state.
Experience an Electric Vehicle at a local ride & drive, learn about state and utility incentives, and access tools, training, and other resources for dealerships and commercial fleets across the state.
The Vision:
ESTABLISH EV CROSSROADS
 Create Indiana’s largest working group of EV stakeholders, such as charging suppliers, vehicle manufacturers, certified dealerships, and consumer groups to support electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Create Indiana’s largest working group of EV stakeholders, such as charging suppliers, vehicle manufacturers, certified dealerships, and consumer groups to support electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
The Goal:
IMPROVE AIR QUALITY
 Increase the use of alternative fuel technologies through outreach, public-private partnerships, and fleet adoption resulting in reduced transportation related emissions.
Increase the use of alternative fuel technologies through outreach, public-private partnerships, and fleet adoption resulting in reduced transportation related emissions.
Drive Electric Indiana was launched in 2021 and is a statewide project led by Greater Indiana Clean Cities, Inc. The program brings together partners from across the state to align their efforts with the goal of preparing Indiana’s infrastructure, cities, schools, and businesses for the electrification of transportation in Indiana. Since Drive Electric Indiana began, many developments have taken place at the national, state, and local levels, improving conditions and deployment for electric vehicles.
Drive Electric Indiana:
Projects, Events, & Programs
Local Programs:
The collaboration between EV Connect, BIC, and Energy Systems Network (ESN) is to deploy Indiana’s first large-scale Vehicle-to-Grid capable charging system to support school bus fleets, HD trucks, and other customer segment applications. Learn More!
Cummins, Duke Energy, and BCSC collaborated to purchase and install an EV charger at the transportation and maintenance building at Bartholomew at no cost to the school. Duke will do tests, research, and events for three years, and at the end of that time, they hope to hand off the station’s operations to BCSC. Learn more!
Greater Indiana has partnered with the City of Carmel to bring information about EVs to the Carmel community. As more charging stations are being set up and the idea of purchasing an EV becomes more of a reality, we bring our members and partners together for a free event to discuss which EVs are on the market, how to charge them at home and away, what Carmel has been doing to promote EV usage as well as EV charger installation projects, what the Federal National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure program is all about, and how the EV Settlement Grant money is being spent in Indiana. Learn more!
Nationwide Projects & Programs:
This nationwide celebration raises awareness of the many benefits of all-electric and plug-in hybrid electric cars, trucks, motorcycles, and more. Greater Indiana attends these free events across the state to bring information about tax incentives, funding opportunities, and programs such as Indiana’s National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure project to Indiana communities. Learn more!
Greater Indiana is a project partner on the DOE-sponsored Cummins’ MD-HD ZEV Infrastructure Planning Project, focusing on stakeholder engagement, outreach, and providing feedback. This project will develop an extensive two-phase MD-HD EV Charging and H2 Fueling Plan for the Midwest I-80 corridor serving Indiana, Illinois, and Ohio to support 30% of the MD-HD fleet using ZEV technologies by 2035. Learn more!
Greater Indiana is working with the Indiana Department of Transportation (INDOT) and Office of Energy Development to assist with alternative fuel corridor designation and create the state’s EV Infrastructure Deployment Plan under the federal government National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) funding opportunity.
Greater Indiana is an active member and participant in the Midcontinent Transportation Electrification Collaborative (MTEC), facilitated by the Great Plains Institute. MTEC works to increase electric vehicle (EV) use, build infrastructure to support EV travel, decarbonize the transportation sector, and improve air quality and electric system efficiency. MTEC comprises representatives from the state government, electric utilities and cooperatives, charging companies, and environmental organizations. MTEC meets regularly to discuss updates in federal funding programs, rules, and requirements. MTEC participants provide feedback and discuss positions to have a cohesive statement from the group to help guide and inform the federal programs. Learn more!
ALA is working to make transportation pollution-free nationwide. Every year, the ALA generates a report on Driving to Clean Air highlighting that a widespread transition to zero-emission passenger vehicles and electricity would drastically improve health across the United States.
This collaborative represents unprecedented cooperation among Climate Mayors cities across the country to leverage their collective buying power and accelerate the conversion of public fleets to EVs. It is a turnkey, one-stop, online procurement portal providing U.S. cities, counties, courts, school districts, state governments, and public universities equal access to competitively bid EVs and charging infrastructure, innovative financing options and best practices, and other forms of expertise. Sourcewell and Electrification Coalition are program partners on this collaborative.
EV Workforce Development & Manufacturing:
Indiana boasts the highest concentration of manufacturing jobs in the nation and is second in overall automotive production, according to the IEDC. Electric vehicles are supporting jobs and manufacturing in Indiana. Advanced Energy Economy ranked Indiana fourth in the nation for electric transportation employment potential and the EY Mobility Consumer Index predicts that sales of electric vehicles will outpace combustion vehicles by 2036 in the United States, five years sooner than previously expected.
According to an IEA Report, OEMs are expected to embrace electric mobility more widely in the 2020s. Notably, 18 of the 20 largest OEMs, which combined accounted for almost 90% of all worldwide new car registrations in 2020, have announced intentions to increase the number of available models and boost the production of electric light-duty vehicles.
The EV Jobs Hub shows that since 2021, 12 new EV manufacturing and production facilities totaling over $9 billion in EV investments and 5,000 new EV jobs have been announced in Indiana. $4.7 billion of that $9 billion in investments was announced just this year and has opened up the opportunity for 2,606 jobs in the EV industry. 70% of jobs are available in battery manufacturing, meaning there is a critical need for workforce development and training. In the United States, between August 2022 and March 2023, major EV and battery manufacturers announced investments totaling at least $52 billion in EV supply chains in North America.
The 10-member commission is composed of legislative representatives and industry leaders tasked with spearheading the EV movement in Indiana through evaluating existing electric vehicle product facilities and workforce capabilities, identifying training needs and opportunities, assessing the potential creation of training centers, leveraging competencies from the traditional automotive industry for electric vehicle production, identifying growth opportunities, documenting previous instances of manufacturing facility transformations, and recognizing research and development prospects within the electric vehicle product industry. The commission is mandated to submit an annual report to the IEDC and will operate until December 31, 2026. Learn more!
2022 Electrical Vehicle Product Commission Executive Summary
2023 Electrical Vehicle Product Commission Executive Summary
Indiana will be home to two new battery manufacturing facilities in Kokomo and Terre Haute that add up to a $4 billion investment and are predicted to employ more than 2,000 Hoosiers. A $3 billion battery cell plant will also be located in New Carlisle, and it is expected to create 1,700 new jobs.
General Motors Co. is investing $491 million to expand and upgrade its operations in Marion, supporting GM’s EV production. GM is also investing $45 million at its Bedford, Indiana, aluminum die-casting foundry. This investment will expand the facility’s production capacity of EV drive unit castings to support the anticipated strong demand for the Chevrolet Silverado EV and GMC Sierra EV full-size pickups.
Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indiana (TMMI) is investing $803 million to equip the Princeton manufacturing line for two new electric vehicles, one Toyota and one Lexus, officially introducing the Lexus line to TMMI. The investment will also support employee training and supplier re-tooling at supplier facilities.
Electric Vehicles Work for Hoosiers:
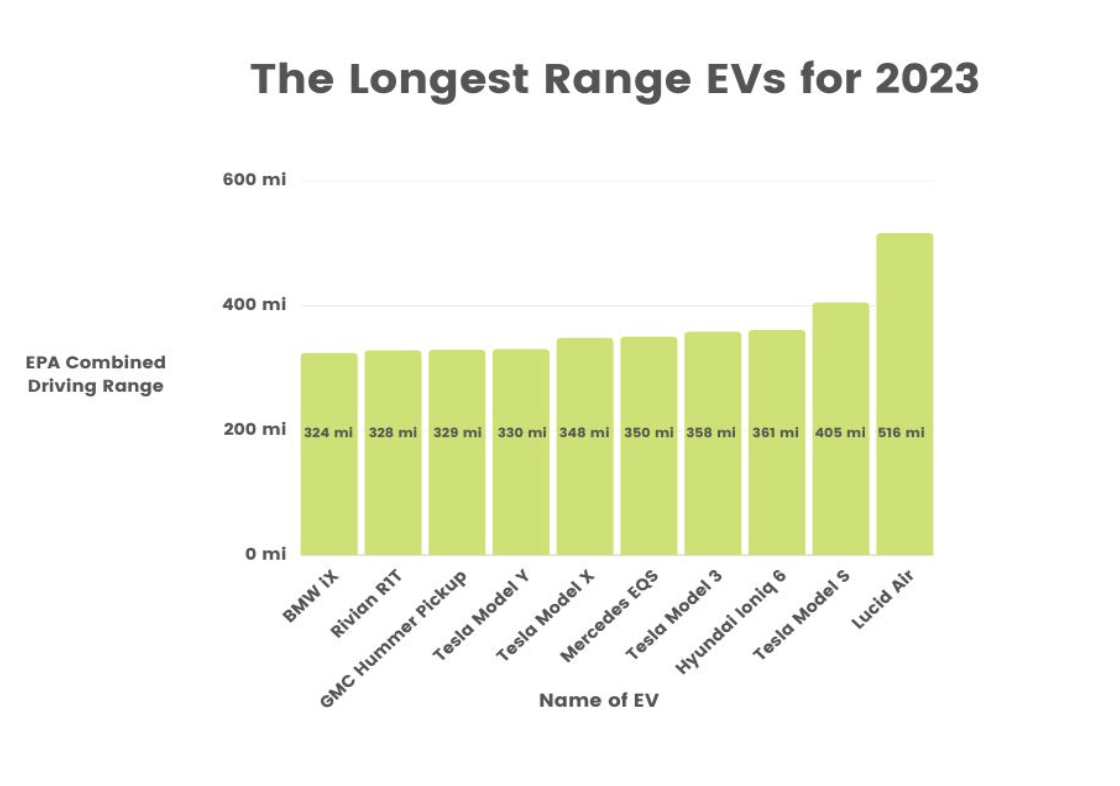
Switching to an electric vehicle doesn’t mean changing your day-to-day lifestyle. The range of modern EVs is enough to cover the average Indiana resident’s weekly commute. When considering an EV, the range is often the first question on your mind. Even the shortest-range EVs are enough to cover daily commutes with charging scheduled for overnight. Use the graph of popular EVs to see which fits your daily driving needs or your next road trip. Use the buyer’s guide to find more ranges and vehicle types to better fit your needs.
Demand for EVs is Rising:
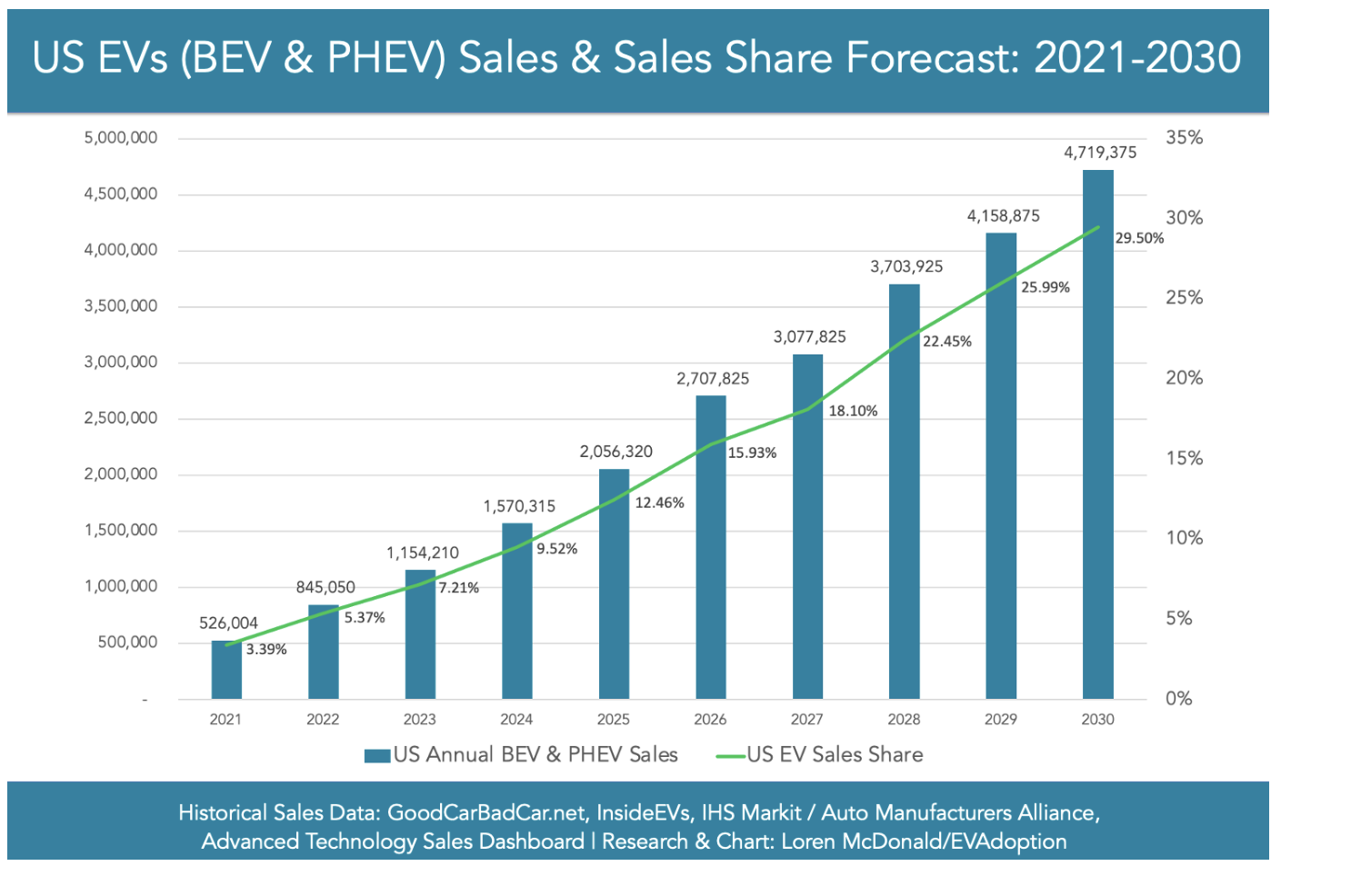
Electric vehicle sales should reach approximately 29.5% of all new car sales in 2030 from an expected 7.21% in 2023. The total number of EV sales will be near 4.7 million in 2030 from 1.1 million in 2023.
The Indiana Office of Energy Development has designed the Indiana Vehicle Fuel Dashboard. This tool is designed to provide public information about the types of vehicle fuels in the state and how it trends over time. In Indiana, the number of registered EV’s and hybrid electric has grown from approximately 10,700 in 2021 to about 15,900 in 2022, about a 39% increase.
Funding Opportunities & Resources:
To stay updated on the latest Notices of Funding Opportunities (NOFOs) and grants, sign up for our newsletter!
Provides grant opportunities that can help meet the community’s transportation infrastructure needs. The Dashboard includes Federal grant programs outside of the DOT and a tool called The DOT Navigator, a resource to help communities understand the best ways to apply for grants and plan for and deliver transformative infrastructure projects and services. Learn more!
INDOT will contract with partners to build Level 3 DC Fast Charge charging stations along Indiana’s federally designated alternative fuel corridors (AFCs). Indiana’s effort feeds into a national initiative to create a network of at least 500,000 reliable chargers across the U.S. to support the growing adoption of electric vehicles. Learn more!
With funding from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, EPA’s new Clean School Bus Program provides $5 billion over the next five years (FY 2022-2026) to replace existing school buses with zero-emission and low-emission models. The CSB involves a rebate and grant program. Eligible activities include the replacement of existing internal-combustion engine (ICE) school buses with electric, propane, or compressed natural gas (CNG) school buses, as well as the purchase of electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) infrastructure and EVSE installations. To ensure a healthy grant competition, this NOFO includes two sub-programs, one for school district and Tribal applicants (School District Sub-program) and one for third-party applicants (Third-Party Sub-program) to serve at least four school district beneficiaries. Learn more!
The $2.5 billion discretionary grant program is divided into two distinct $1.25 billion grant programs to support EV charger deployment over the next five years (FY 2022-2026). The program has two tracks: Corridor Charging: To deploy electric vehicle charging and hydrogen / propane / natural gas fueling infrastructure along designated alternative fuel corridors. Community Charging: To install electric vehicle charging and alternative fuel in locations on public roads, schools, parks, and publicly accessible parking facilities. These discretionary grant programs will ensure charger deployment meets the Biden-Harris Administration priorities, such as supporting rural charging, building resilient infrastructure, climate change, and increasing EV charging access in underserved and overburdened communities. Learn more!
The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) Federal Transit Administration Low or No Emission (Low-No) Vehicle Program provides $5.6 billion over 5 years (FY 2022–2026) to help modernize bus fleets and bus facilities across the country, focused on helping transit agencies purchase or lease low- or no-emission vehicles and necessary charging or fueling infrastructure. Learn more!
The EPA is authorized under the Diesel Emissions Reduction Act (DERA) to offer funding assistance to accelerate the upgrade, retrofit, and turnover of the legacy diesel fleet. The program provides $100 million annually for the next five years (FY 2023-2029). Learn more!
The U.S. Department of Transportation’s (DOT) Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) EV Charger Reliability and Accessibility Accelerator is offering $100 million for funding for the repair and replacement of existing, non-operational publicly accessible Level 2 and direct current fast charging (DCFC) stations.The National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program stipulates a 10% set-aside of the $5 billion created by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and administered by the Federal Highway Administration to provide grants to states and localities that require additional assistance to strategically deploy EV charging infrastructure. Learn more!
Indiana’s Utilities Offer Benefits to EV Owners:
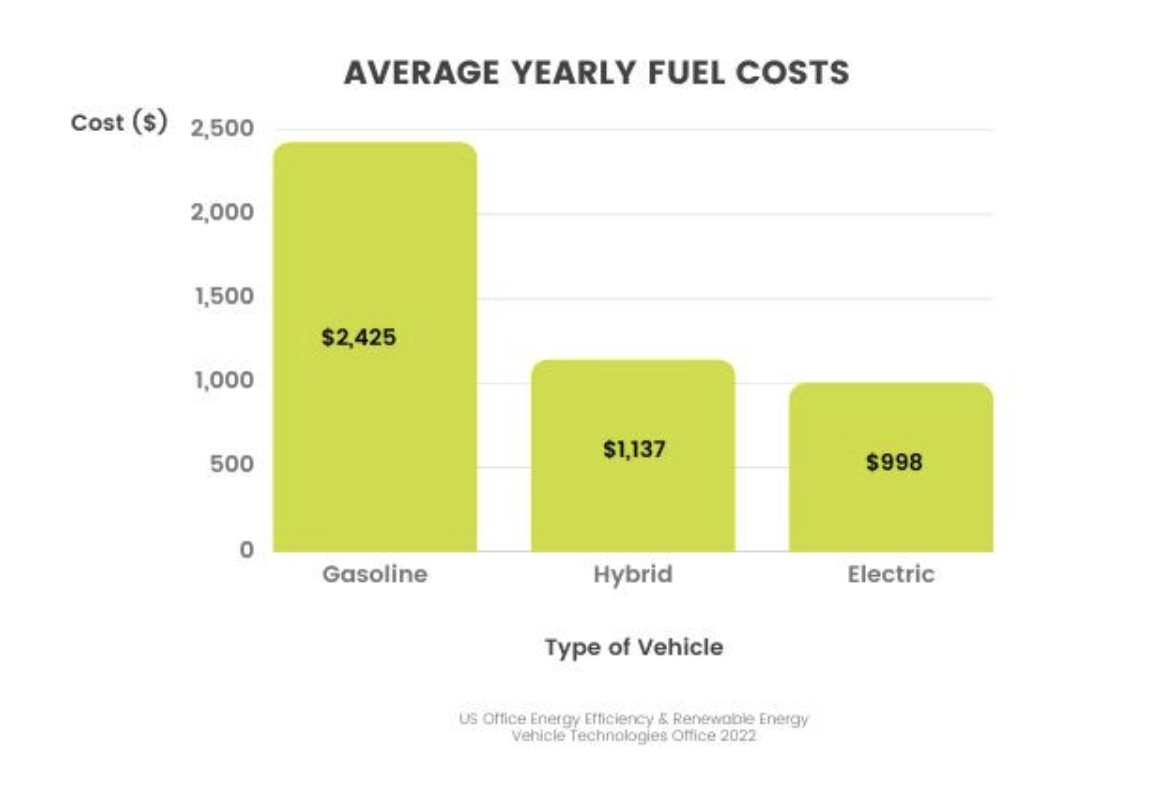
Driving an EV saves money on fuel. Utilities and local power providers are leading Indiana’s transition to electric vehicles by offering access to vehicles, incentives, and special electric rates. EV owners benefit from reduced or fixed electric rates during “Time of Use” (TOU) periods known as “Off-Peak” hours. Charging an EV overnight during “off-peak” hours will reduce the load on the grid and your price per Kilowatt Hour. Check your local power provider to see incentives and rates.
Indiana Utility Benefits & Rates:
Find your utility below to see what benefits they offer, their time-of-use hours, and contact information for further research.
 Indiana Michigan Power offers a time-of-use (TOU) rate to residential customers for PEV. TOU rate off-peak hours are between 11 pm and 6 am, Monday through Friday, and all-day Saturday and Sunday. Indiana Michigan Power may require customers to install a metering system that is capable of separately tracking PEV charging. Acess the I&M Charge at Home information.
Indiana Michigan Power offers a time-of-use (TOU) rate to residential customers for PEV. TOU rate off-peak hours are between 11 pm and 6 am, Monday through Friday, and all-day Saturday and Sunday. Indiana Michigan Power may require customers to install a metering system that is capable of separately tracking PEV charging. Acess the I&M Charge at Home information.
Indiana Michigan Power’s IM Plugged In Program offers rebates for businesses, fleets, and multi-unit buildings. Participating customers may be eligible to receive a one-time enrollment rebate of $250 for 240-volt wiring and/or Level 2 EV charger with proof of qualifying purchase or a 5-year revenue credit through Contribution In Aid of Construction.
Small Commercial Business Incentives: Existing small-commercial customers who average less than 4,500 kWh per month of electricity are eligible for a $500 incentive and a discounted off-peak rate of up to a 45% reduction from the standard rate.
Commercial and Industrial: Indiana Michigan Power can pay $2,500 for the first port and $500 for each additional port toward the installation of PEV charging equipment.
Access the I&M Charge at Work information.
![]() The Indianapolis Power & Light Co is now AES Indiana and offers special EV charging rates, including year-round time-of-use (TOU) for residential and business customers who own a licensed PEV. By participating in the EV Managed Charging Program, you help reduce your fossil fuel footprint and prevent overloading the energy grid. Customers who are considering purchasing Level 2 electric vehicle supply equipment should contact IPL to discuss the benefits and requirements of participating in the program. AES Indiana offers EV Managed Charging Program. By participating in the EV Managed Charging Program, you help reduce your fossil fuel footprint and prevent overloading the energy grid. Access AES Electric Vehicles information.
The Indianapolis Power & Light Co is now AES Indiana and offers special EV charging rates, including year-round time-of-use (TOU) for residential and business customers who own a licensed PEV. By participating in the EV Managed Charging Program, you help reduce your fossil fuel footprint and prevent overloading the energy grid. Customers who are considering purchasing Level 2 electric vehicle supply equipment should contact IPL to discuss the benefits and requirements of participating in the program. AES Indiana offers EV Managed Charging Program. By participating in the EV Managed Charging Program, you help reduce your fossil fuel footprint and prevent overloading the energy grid. Access AES Electric Vehicles information.
 Duke Energy offers one of the lowest electricity costs in the Midwest. Charging your electric vehicle at home is inexpensive and convenient. You’ll be able to charge at the standard residential electric rate, which varies but is typically less than fuel costs.
Duke Energy offers one of the lowest electricity costs in the Midwest. Charging your electric vehicle at home is inexpensive and convenient. You’ll be able to charge at the standard residential electric rate, which varies but is typically less than fuel costs.
Residential Programs
Charger Solution: Customers can rent a level 2 EV charger for their home and pay a flat rate each month
Off-Peak Charging Credit: Eligible EV drivers who charge at night and during off-peak hours can earn up to $200 in annual bill credits
Business Programs
Charger Solution: Customers can rent a level 2 or DC Fast EV charger for their home and pay a flat rate each month
Commercial Charger Rebate: Earn attractive rebates when you apply before installing a Level 2 EV charger at your business
Fleet Electrification Advisory Service: Receive a custom road map, recommendations from industry experts, and meet your goals with less environmental impacts
Access Duke Energy’s Electric Vehicle information.
Electricity Co-operatives and Rural Electric Membership Corporations (REMC) offer non-metropolitan and rural communities the opportunity to develop and own their own electricity. Unlike investor-owned utilities, profits are reinvested or redistributed to the company. Contact your Indiana Co-op and REMC to find out how they are preparing for electric vehicles.

Electric Vehicle Tax Incentives & Credits:
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (Public Law 117-169) amended the Qualified Plug-in Electric Drive Motor Vehicle Credit (IRC 30D), now known as the Clean Vehicle Credit, and added a new requirement for final assembly in North America that took effect on August 17, 2022. This final assembly requirement applies for new electric, fuel cell electric, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles acquired, delivered, and placed in service after August 16, 2022. For vehicles placed in service on or after January 1, 2023, the Clean Vehicle Credit provisions are subject to updated guidance from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
Starting January 1, 2024, the most significant change to the Clean Vehicle Tax Credit is:
Under the Inflation Reduction Act, consumers can choose to transfer their new clean vehicle credit of up to $7,500 and their previously owned clean vehicle credit of up to $4,000 to a car dealer
Starting January 1, 2023, the most significant changes to the Clean Vehicle Tax Credit are:
New clean vehicles are eligible for up to $7,500 depending on battery size until further guidance from the Treasury/ IRS is released in March 2023
Full list of vehicles that qualify for the tax credit
Previously owned clean vehicles (also known as “used vehicles”) are eligible for a tax credit of up to $4,000
The Alternative Fuel Refueling Property tax credit is extended until December 31, 2032
New EV Credit Rule coming in 2024
The minimum battery capacity must be 7-kilowatt hours
Vehicles must be made by a qualified manufacturer
MSRP limitations apply
Income limits apply to taxpayers
The taxpayer must report the vehicle identification number (VIN) of the vehicle on the taxpayer’s income tax return
Dealers must provide reports to the taxpayer and the IRS regarding the sale of the vehicle
Manufacturers and Models for New Qualified Clean Vehicles Purchased in 2023 or After
Access current federal tax incentives for your next vehicle purchase.
Electric Vehicles Ready for Indiana Fleets:
Electric vehicles come in all shapes and sizes. See how schools, municipalities, and businesses are benefiting from adding electric vehicles to their fleets to reduce fuel and maintenance costs. Contact the Drive Electric Indiana team to address your unique fleet needs.
 The Atlas EV Hub has an EV Charging Financial Analysis Tool that equips users with critical information on the financial performance of electric vehicle charging projects. The tool uses the discounted cash flow method to evaluate the financial performance of a charging project through a variety of revenue streams over the lifetime of the charging equipment. The tool was originally developed by the Cadmus Group in partnership with the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions as part of a study commissioned by the Washington State Legislature’s Joint Transportation Committee to identify business models for financially sustainable, private-sector-funded charging networks.
The Atlas EV Hub has an EV Charging Financial Analysis Tool that equips users with critical information on the financial performance of electric vehicle charging projects. The tool uses the discounted cash flow method to evaluate the financial performance of a charging project through a variety of revenue streams over the lifetime of the charging equipment. The tool was originally developed by the Cadmus Group in partnership with the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions as part of a study commissioned by the Washington State Legislature’s Joint Transportation Committee to identify business models for financially sustainable, private-sector-funded charging networks.
Another tool the Atlas EV Hub has developed is The Fleet Procurement Analysis Tool. This tool equips users with decision-relevant information on the financial viability and environmental impact of light-, medium-, and heavy-duty vehicle fleet procurements. The tool compares procurements side-by-side on a cost-per-mile basis and provides an analysis of cash flows and location-specific lifecycle emissions.
Dashboard for Rapid Vehicle Electrification (DRVE) is a tool created by the Atlas EV Hub and Electrification Coalition that equips users with decision-relevant information on the financial viability and environmental impact of light-, medium-, and heavy-duty vehicle fleet procurements across an entire fleet. The tool allows users to import all fleet vehicles and compare a fleet’s conventional vehicles with an electric vehicle alternative.
The Electrification Coalition possesses EV Tools and Calculators Clearinghouse to assist you in analyzing your own fleet. From interactive programs to input your personalized fleet metrics to guides and articles to support your research efforts.
The Department of Energy’s Clean Cities Program has enlisted the expertise of Argonne to develop the Alternative Fuel Life-Cycle Environmental and Economic Transportation (AFLEET) Tool for Clean Cities stakeholders to estimate petroleum use, greenhouse gas emissions, air pollutant emissions, and cost of ownership of light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles using simple spreadsheet inputs to examine both the environmental and economic costs and benefits of alternative fuel and advanced vehicles.
Heavy-Duty Vehicle Resources:
The North American Council for Freight Efficiency (NACFE) hosts Run on Less – Electric Depot, a demonstration of zero-emissions commercial vehicles, showcased electric vehicles operating in four market segments including vans, and step vans, medium-duty box trucks, terminal tractors, and heavy-duty regional haul tractors.
The Green Transportation Summit & Expo (GTSE) is the West Coast’s premier fleet modernization and sustainable transportation event. GTSE offers attendees an inside look at the latest in fleet technologies and innovation and provides informative sessions featuring a who’s who of national and regional transportation leaders. Learn more!
The Electric School Bus Initiative released their 2023 Electric School Bus Market Study and Electric School Bus U.S. Buyer’s Guide. A comprehensive guide offering school districts and others an overview of the electric school bus market and a catalog that presents electric school bus models available today with detailed vehicle specifications.
Support Indiana’s Sustainable Future:
With the construction of a Class 2 structure, the building must be designed, constructed, and wired to enable an occupant of the structure to charge an EV through the use of EVSE by the occupant or a third party. Learn more!
Referred to Committee on Roads and Transportation on January 12, 2023
Requires the Comptroller General of the United States to analyze the costs of converting light-duty vehicles in the Federal fleet to electric vehicles for other purposes. Learn more!
Referred to the Subcommittee on Environment, Manufacturing, and Critical Materials on February 17, 2023
Requires the state agency that oversees utilities to consider five things in most of its decisions: reliability, affordability, resiliency, stability and environmental sustainability. The bill also cuts in half the amount of power utilities can buy from the grid during peak demand. Learn more!
Became public law 55 on April 20, 2023
Individuals who own EV charging stations and make them available for public consumption would be authorized to charge users in whole or in part based on the kilowatt-hours of electricity sold, while clarifying this doesn’t make the person a public utility. Learn more!
Became public law 94 on March 11, 2022
The Funding Indiana’s Roads For a Stronger, Safer Tomorrow (FIRSST) Task Force— a group created by the Legislature—is expected to gather information about the way Indiana pays for road construction and improvements. Its mission is to provide recommendations to the Legislature for its 2024 session. Learn more!


